Comprehensive Guide to Healthy Food and Nutrition
Healthy eating is one of the most fundamental aspects of a long and productive life. A balanced diet rich in whole, natural foods not only supports physical health but also boosts mental performance, strengthens immunity, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. In an age of fast food and ultra-processed snacks, returning to nutritious, whole foods is more essential than ever.

What is Healthy Food?
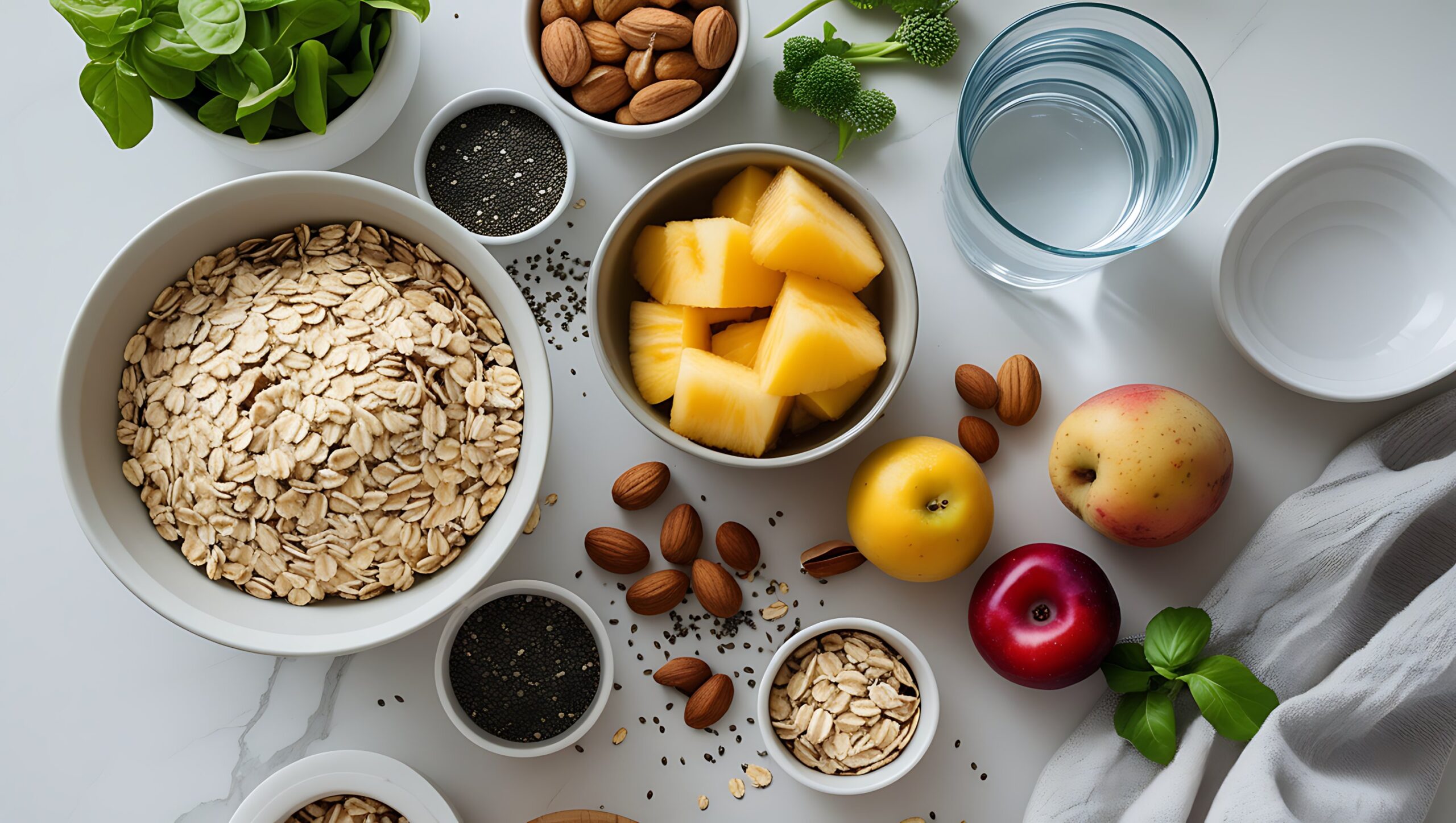
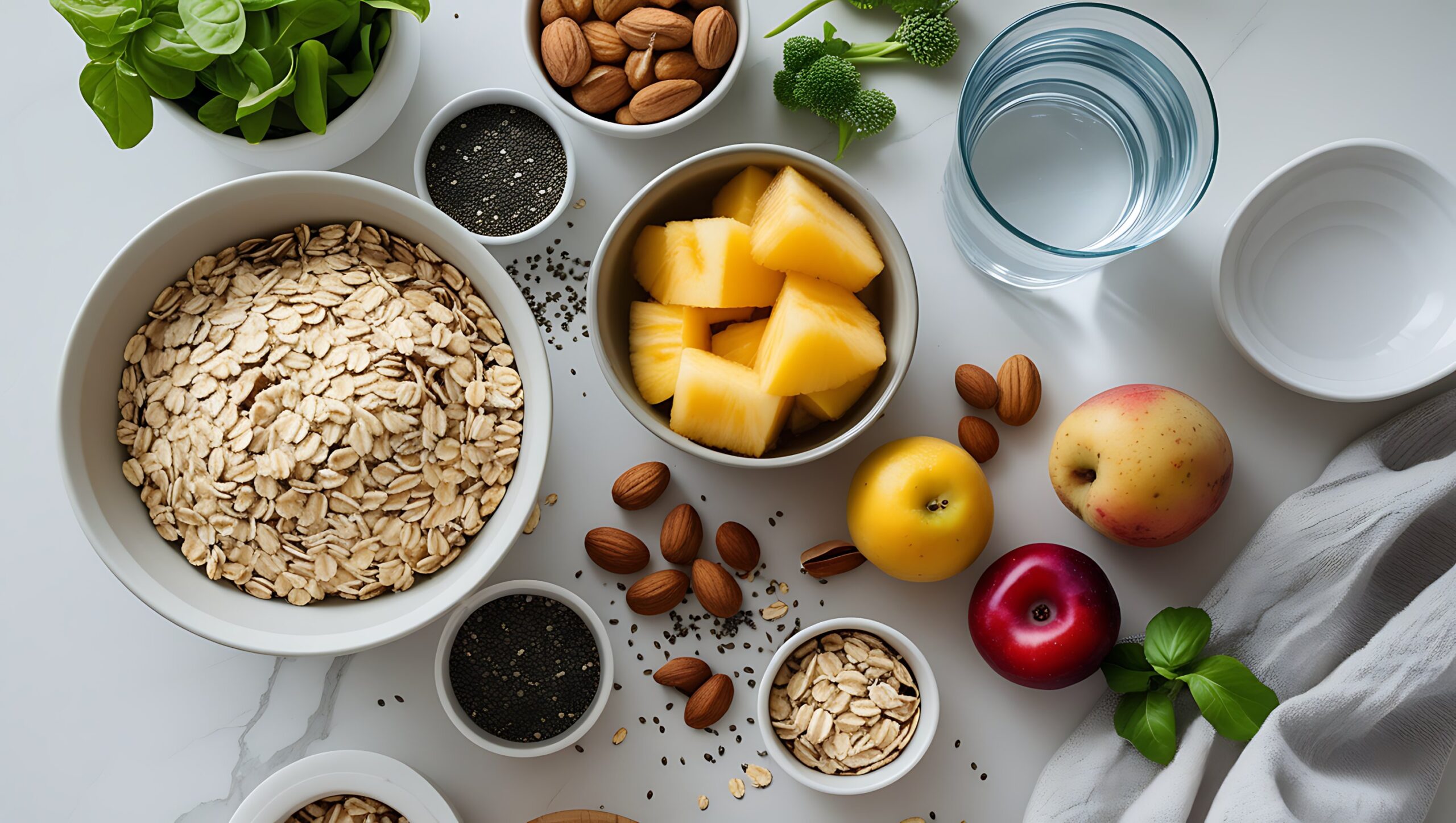
Healthy food refers to natural, minimally processed foods that deliver essential nutrients—macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals)—needed for optimal body function. These foods provide energy, promote development, and help the body repair and regenerate cells.
The core of healthy eating revolves around a variety of food groups:
- Fruits and Vegetables: High in vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, they lower inflammation and reduce disease risk.
- Whole Grains: Retain their bran and germ, providing fiber, B vitamins, iron, and magnesium.
- Lean Proteins: Support muscle growth, immune response, and tissue repair.
- Healthy Fats: Found in nuts, seeds, avocado, and fish, these support heart health and hormone balance.
- Water: Vital for digestion, circulation, temperature regulation, and detoxification.
The Scientific Benefits of Eating Healthy
Scientific studies consistently show that diets rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods lower the risk of chronic diseases and support overall health. Here are some of the top evidence-based benefits:
1. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Diets high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are associated with a significantly lower risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), up to 80% of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes and 40% of cancers could be prevented with improved nutrition and lifestyle.
2. Weight Management
Healthy foods are naturally lower in calories and higher in fiber and protein, which promote fullness and prevent overeating. Diets focused on unprocessed food sources reduce cravings and help regulate body weight.
3. Stronger Immune System
Vitamins A, C, D, and E, along with zinc and selenium—found in colorful fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds—play critical roles in immune defense. A well-balanced diet helps your body fight infections and recover faster.
4. Enhanced Brain Function
Omega-3 fatty acids (from fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds), antioxidants, and B vitamins are key to memory, learning, and mood regulation. Nutritional psychiatry studies show a strong link between diet and mental health.
5. Healthy Digestion
Whole plant-based foods support gut health due to their fiber content, which nourishes beneficial bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome influences immunity, metabolism, and even mental well-being.

Understanding Nutrient Density vs. Empty Calories
Nutrient-dense foods deliver high levels of vitamins, minerals, and fiber per calorie. Examples include leafy greens, berries, eggs, sweet potatoes, and legumes. In contrast, foods high in “empty calories” (soda, chips, candy, fast food) offer little to no nutritional value and often lead to weight gain and poor health outcomes.
Tip: A good rule of thumb is to eat foods that are as close to their natural state as possible. If it comes in a box and has ingredients you can’t pronounce, it’s probably not healthy.
Barriers to Healthy Eating
Despite knowing the benefits, many people struggle to eat healthily due to:
- Time Constraints: Busy schedules lead people to rely on convenience foods.
- Cost: Whole foods can be perceived as more expensive, though this is often a misconception.
- Food Deserts: Many low-income areas lack access to fresh produce and whole grains.
- Lack of Education: People may not understand what constitutes a balanced diet or how to prepare healthy meals.
Practical Tips for Eating Healthier
Adopting healthier eating habits doesn’t require drastic changes. Here are practical, sustainable strategies:
- Start Small: Replace one processed meal a day with a homemade one featuring vegetables and lean protein.
- Meal Prep: Preparing meals ahead of time saves money, reduces stress, and avoids unhealthy takeout.
- Read Labels: Watch for added sugars, hydrogenated oils, and excessive sodium.
- Eat the Rainbow: Choose a variety of fruits and vegetables to ensure diverse nutrients.
- Hydrate: Start your day with a glass of water and limit sugary beverages throughout the day.
Conclusion: A Long-Term Investment in Health
Eating healthy is not a short-term fix; it’s a lifelong approach to well-being. A diet rich in whole, natural foods not only prevents disease but also enhances energy, focus, and longevity. By making small, consistent changes in what you eat, you can profoundly impact your quality of life. Health is built on daily choices—start with your plate.
References