Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
What Is Heart Disease?
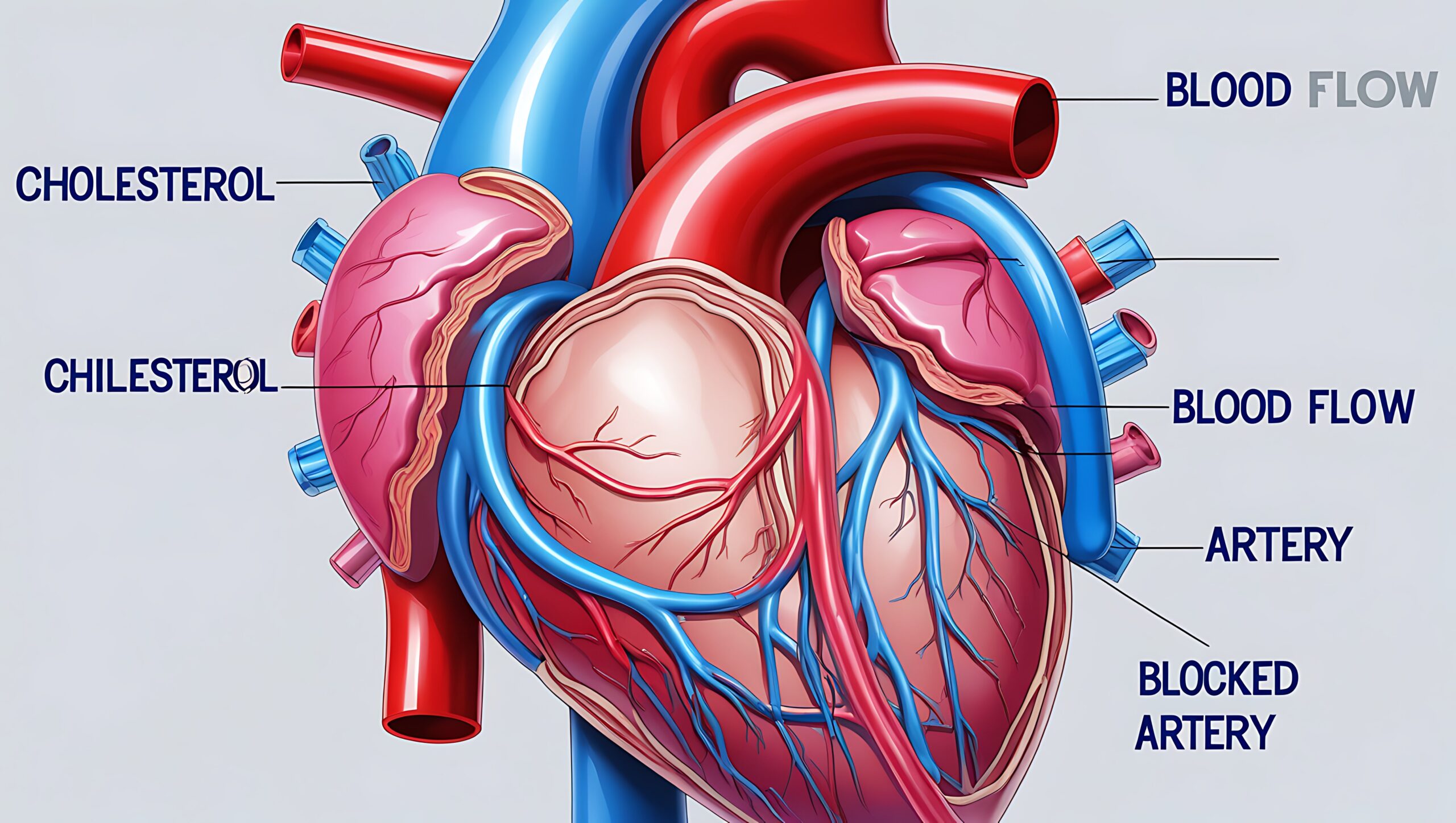
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease (CVD), refers to a range of conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels. These include coronary artery disease, heart failure, arrhythmias, and congenital heart defects. It remains the leading cause of death globally, responsible for nearly 18 million deaths each year, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Heart disease develops due to several modifiable and non-modifiable factors. High blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and physical inactivity are key contributors. Non-modifiable risk factors include age, family history, and gender. Men are typically at higher risk at a younger age, while women face increased risk post-menopause.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of heart disease can vary based on the specific condition but commonly include chest pain or discomfort (angina), shortness of breath, fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and swelling in the legs or feet. Some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms until a serious event like a heart attack or stroke occurs.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Preventing heart disease involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes per week), avoiding tobacco, moderating alcohol consumption, managing stress, and undergoing regular health screenings are all crucial.
Treatment Options
Treatment for heart disease may include lifestyle modifications, medications, and in some cases, surgical procedures. Common medications include statins, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and antiplatelet drugs. In advanced cases, procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be required to restore blood flow and reduce complications.
Heart Health: A Lifelong Commitment
Managing heart disease is a lifelong commitment. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, medication adherence, lifestyle adjustments, and mental well-being play vital roles in maintaining cardiovascular health and enhancing quality of life.
References
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases. https://www.who.int
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Heart Disease Facts. https://www.cdc.gov
- American Heart Association. Prevention and Treatment of Heart Disease. https://www.heart.org
- Mayo Clinic. Heart Disease. https://www.mayoclinic.org